🧠 What Is Hawk-Eye in Cricket?
Hawk-Eye is cricket’s AI-powered ball-tracking system.
It captures, calculates, and predicts the ball’s path with millimeter accuracy.
Six or more high-speed cameras are placed around the ground. They record every frame, then create a 3D map of the ball’s journey — from the bowler’s hand to the pad.
It’s the secret behind those colorful DRS animations that decide whether a batsman is out or safe.
🎯 Why LBW Needs Hawk-Eye
LBW (Leg Before Wicket) decisions used to depend purely on human vision.
But when the ball swings or seams at 140 km/h, even trained eyes can miss the final destination.
Hawk-Eye removes guesswork.
It shows where the ball pitched, hit, and would’ve gone next — turning uncertainty into precision.
🏏 Step-by-Step: How Hawk-Eye Works for LBW
1️⃣ Capture
Six high-speed cameras record the ball in motion from different angles.
2️⃣ Track
Software identifies the ball in every frame and builds its real 3D path.
3️⃣ Impact
When the ball hits the pad, Hawk-Eye freezes that impact point — marking exactly where contact happened.
4️⃣ Predict
Using physics — gravity, speed, swing, spin — the system projects the path the ball would’ve taken if it hadn’t hit the pad.
5️⃣ Decide
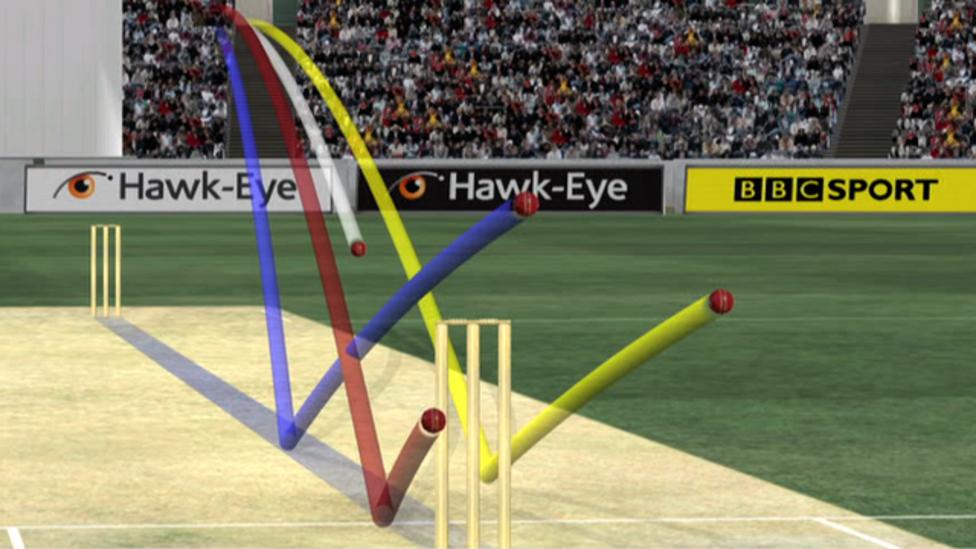
Finally, it shows the visual projection on screen:
- Blue dot = pitching
- Red = impact
- Yellow line = predicted path
If the ball is hitting the stumps → OUT.
If it’s just brushing → Umpire’s Call.
⚖️ What Is Umpire’s Call?
It’s cricket’s “benefit of doubt” rule.
If the projection only marginally touches the stumps, the on-field umpire’s decision stands.
That’s why the same delivery might be “out” in one match and “not out” in another — it depends on the original call.
📊 How Accurate Is Hawk-Eye?
According to tests, Hawk-Eye’s margin of error is around 2.6 millimeters.
That’s smaller than the stitching on a cricket ball!
Still, small assumptions — like ball rotation or swing after impact — can cause rare disputes.
In early 2024, Ben Stokes criticized an LBW call against Zak Crawley, saying the ball “looked wrong” on the replay.
Moments like that keep the debate alive.
🚨 What’s New in 2025?
In IPL 2025, Hawk-Eye has been upgraded to judge wides — both off-side and head-high balls.
It adjusts automatically to the batter’s movement, measuring line and height in real time.
So the next time a wide is called, it’s not opinion — it’s AI measurement.
💡 Recap in One Glance
| Step | Process | What Happens |
| 1 | Capture | Cameras record every frame |
| 2 | Track | 3D path of ball is built |
| 3 | Impact | Exact pad contact is marked |
| 4 | Predict | Path beyond impact is simulated |
| 5 | Decide | Umpire or DRS shows final result |
🏁 Final Thoughts
Hawk-Eye has changed cricket forever.
It made LBW reviews faster, clearer, and fairer — though still not flawless.
Next time you see that red line hitting the stumps on TV, remember: you’re watching AI, physics, and precision cameras deciding the fate of a wicket.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What is the accuracy of Hawk-Eye in cricket?
Hawk-Eye’s average error margin is about 2.6 mm, making it one of the most precise sports tracking systems in the world.
Q2. Can Hawk-Eye make mistakes?
Yes, though rare. Errors can occur if the system misidentifies the impact frame or if the ball’s swing/spin changes suddenly after impact.
Q3. What does “Umpire’s Call” mean in LBW?
It means the on-field umpire’s decision stands because the prediction was too close to call — usually when less than half of the ball would hit the stumps.
Q4. Who developed Hawk-Eye?
Hawk-Eye was invented by Dr. Paul Hawkins in the early 2000s and is now owned by Sony Sports Technologies.
Q5. Is Hawk-Eye used for other sports?
Yes! It’s used in tennis (line calls), football (goal-line tech), and snooker (shot tracking) too.